In this blog, we will discuss DBMS job scheduler via Oracle Integration Cloud and how it can be accomplished.
DBMS SCHEDULER
This is a server-based scheduler, so everything is done in the context of the database server. It is nothing to do with scheduling things on a client PC.
Difference between DBMS_JOB and DBMS_SCHEDULER
| DBMS_JOB | DBMS_SCHEDULER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. What can the scheduler do?
The Scheduler supplies complex enterprise scheduling functionality, which you can use to:
- 1. Schedule job execution based on time or events.
- 2. Schedule job processing in a way that models your business requirements.
- 3. Manage and inspect jobs.
- 4. Execute and manage jobs in a clustered environment.
2. How does DBMS_SCHEDULER work?
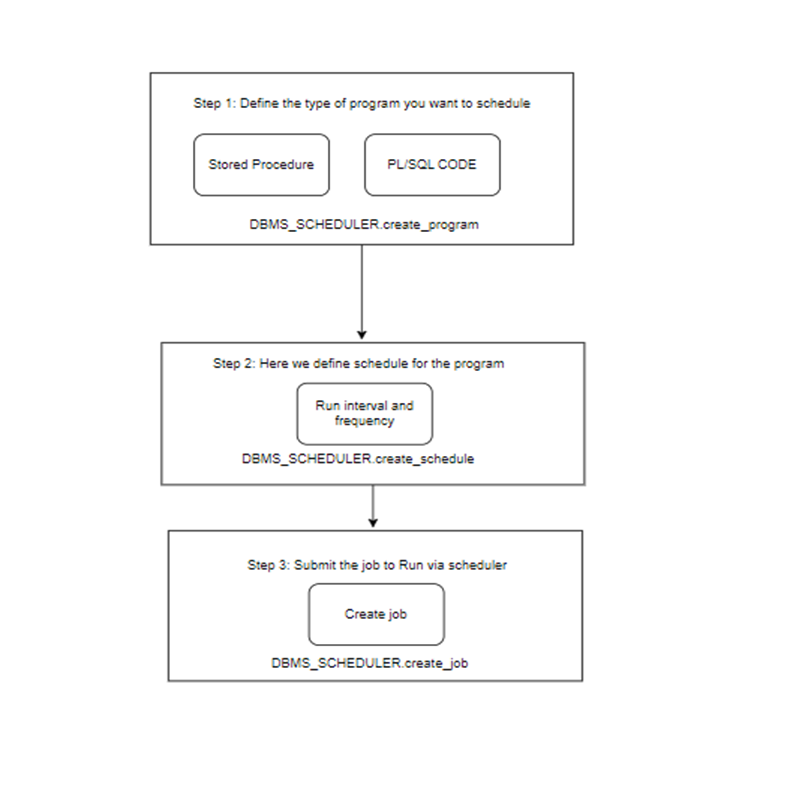
We can use DBMS_SCHEDULER in 3 separate ways.
- 1. First, we must define a program using PL/SQL or STORED PROCEDURE. (DBMS_SCHEDULER.CREATE_PROGRAM)
- 2. Next, we need to define a schedule for the above program.(DBMS_SCHEDULER.CREATE_SCHEDULE)
- 3. Finally, we need to create a job. Using the program name and schedule it uses the second step.(DBMS_SCHEDULER.CREATE_JOB)
3. How to create and run a job in Oracle?
- A job is a collection of metadata that describes a user-defined task that is scheduled to run one or more time.
- It is a combination of what needs to be executed(program) and when to run(schedule) along with any other arguments required by the program.
- Job is completely self-contained depending on which overloaded of the CREATE_JOB procedure is used to create them.
- Jobs are normally run asynchronously under the control of the job co-ordinator.
Note: You must have the CREATE_JOB privilege to create a job in own schema and create any job privilege to create a job in any schema except SYS.
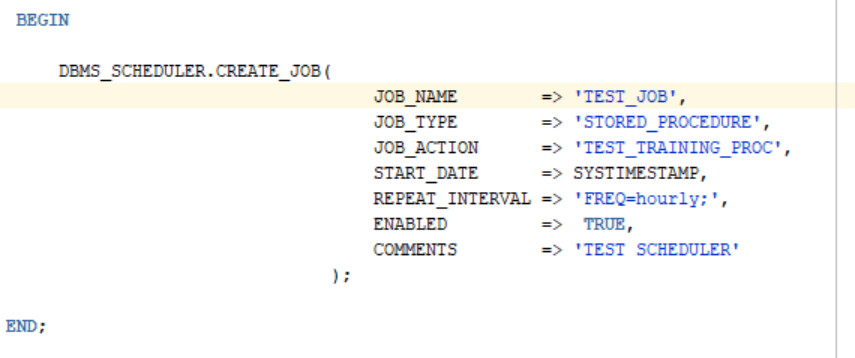
a.) 1. create_job
We can directly write a job which includes both program and schedule. No need to create program and schedule separately.
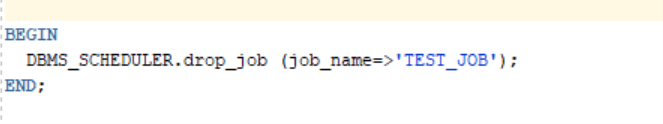
a.) 2. For drop a job
Jobs can be dropped using the DROP_JOB procedure.
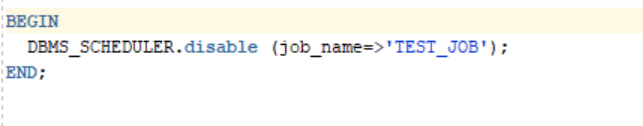
a.) 3. For disabling a job
Applicable jobs can be disabled using DISABLE procedure.
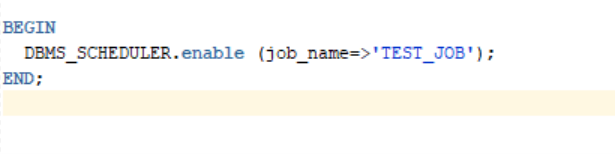
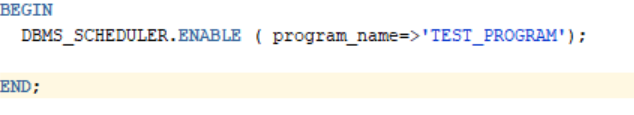
a.) 4. To enable a job
Applicable jobs can be enabled using ENABLE procedure.
a.) 5. We can use the RUN procedure to start a job right away.

a.) 6. To stop a running job, we can use the STOP procedure.

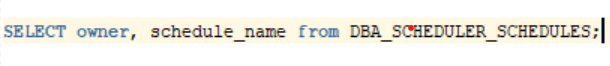
a.) 7. View schedule details
To see schedule details, you must use DBA_SCHEDULER_SCHEDULES query
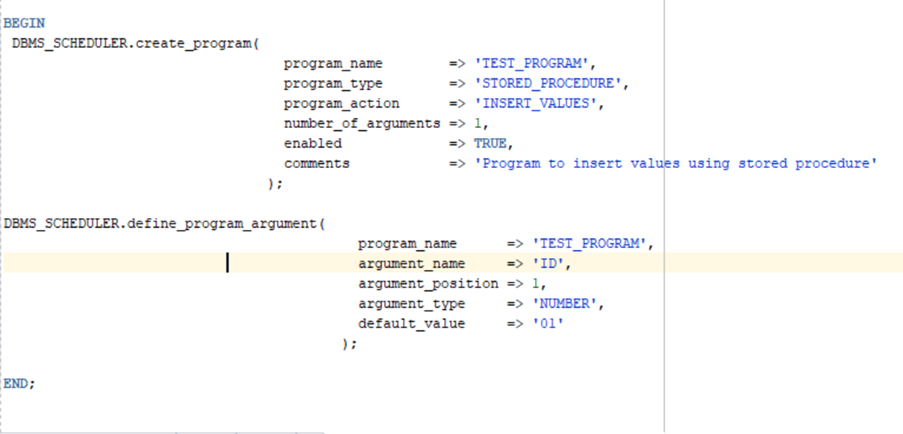
Note: If we are not using Create job procedure, then we need to create program followed by schedule procedure separately.
b.) DBMS_SCHEDULER.create_program and program argument
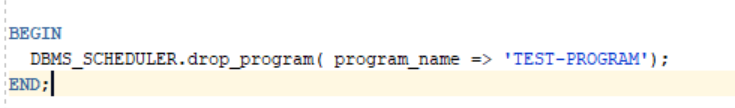
b.) 1. To drop a program
Program can be dropped by using the DROP procedure.
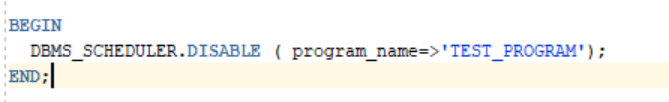
b.) 2. To disable a program
Program can be disabled by using DISABLE procedure.
b.) 3. To enable a program
To enable a program, we can use ENABLE procedure.
c.) DBMS_SCHEDULER.create_schedule
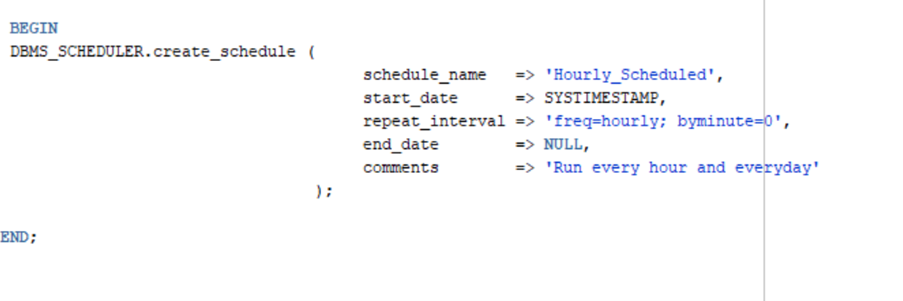
Repeat interval using calendaring syntax
a.) Every day:
‘Freq= daily;’
b.) Every day, at midnight:
‘Freq=daily; by hour=0; by minute=0; by second=0;’
c.) Every day, at 06:00:
‘Freq=daily; by hour=6; by minute=0; by second=0;’
d.) Every hour:
Freq=hourly;
e.) Every hour, on the hour:
Freq=hourly; by minute=0; by second=0;
f.) Every minute:
Freq=minutely;
g.) Every Monday, at 09:00:
Freq=weekly; by day=Mon; by hour=9; by minute=0; by second=0;
h.) First Monday of each quarter:
Freq=monthly; by month=1,4,7,10; by day=1Mon;
Several types of job States:
- Completed- Job completed not scheduled to run again.
- Stopped- Job scheduled to run once and was stopped during its run.
- Succeeded- Job scheduled to run once and completed successfully.
- Failed- Job scheduled to run once and failed.
- Running- Job is currently running.
- Scheduled- Job is scheduled to be executed.
- Disabled- Job is disabled.
- Broken- Job is broken and has issues.
Why do we use DBMS_SCHEDULER via OIC?
Ans: We use the DBMS_SCHEDULER via OIC because, there is no need to wait for long running processes. OIC has a response time limit of four minutes. Also, it is reusable and easy to use. Also, it is reusable and easy to use.
Related article: How To Burst Large Data Files Using Chunk Or Split By From Oracle BI Report?
Problem: How to run a procedure from OIC to Database
Solution: Steps to create OIC connection for DB adapter.
Step 1: Log in to the OIC Instance with valid credentials.
Step 2: Select DBaaS adapter under connection.
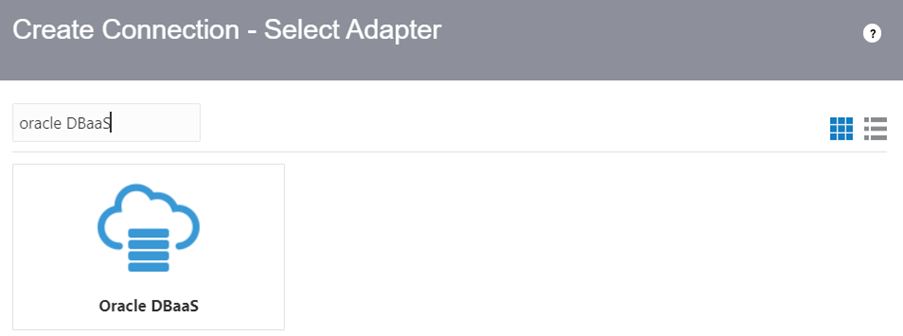
Step 3: Supply all the necessary credentials to connect the adapter.
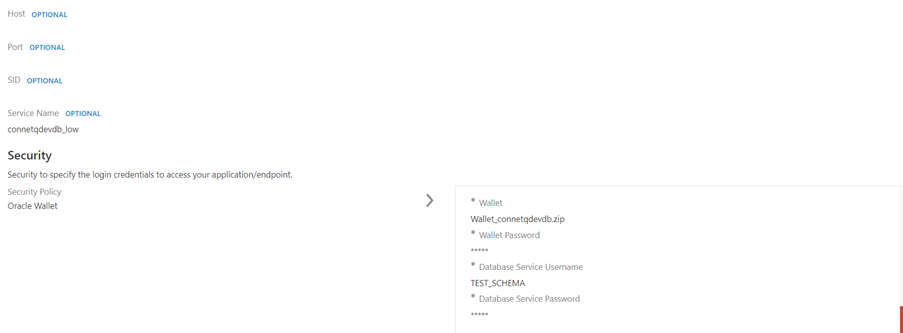
Note: Before using the connection test it and save it.
Step 4: Add DB connection in the integration and select the operation as Invoke a stored procedure.
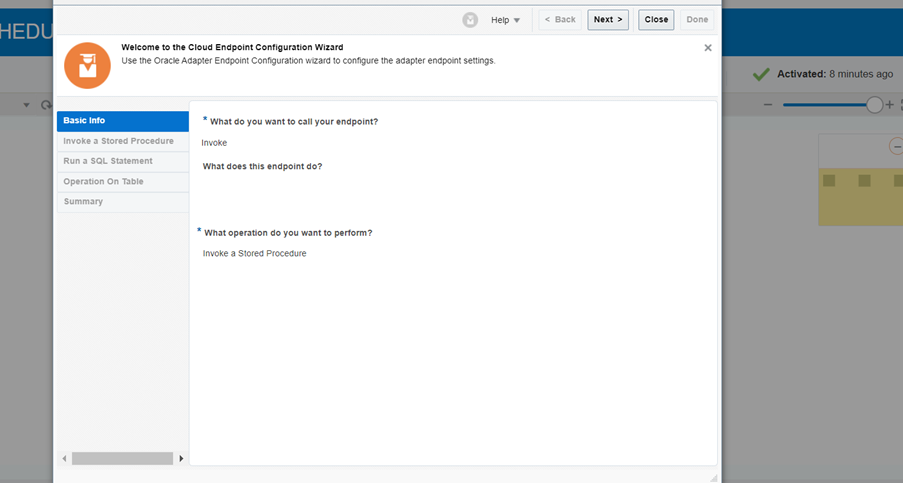
Step 5: Select the Schema name and choose the Procedure , which we create in Database.
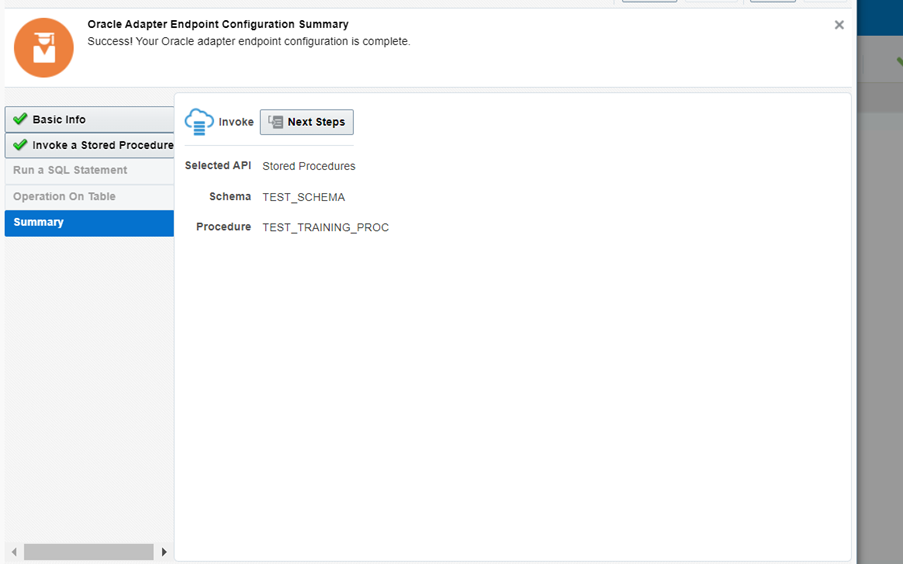
Step 6: Save the integration and test it.
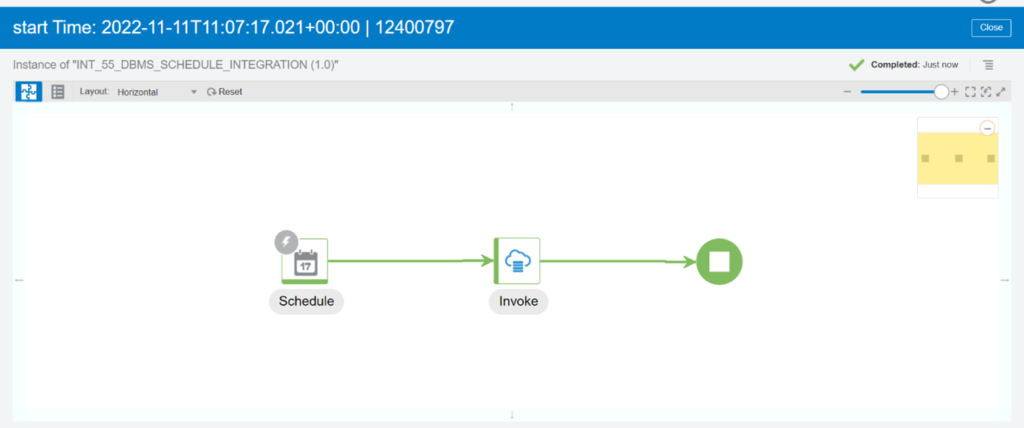
In this blog, we have successfully shared how to run and use a DBMS Scheduler via OIC. If you have any questions regarding this blog, you can get in touch with us at Conneqtion Group.