In the current business landscape, companies are actively exploring ways to cut costs and improve operational efficiency. By outsourcing application management, companies can allocate their internal IT resources to concentrate on essential business activities while gaining access to specialized knowledge and skills. Let’s explore the benefits and challenges faced by organizations.
What is an application management service (AMS) and its role?
An Application Management Service (AMS) refers to the outsourcing of the support of applications and software systems to a third-party service provider. It involves entrusting the responsibility of monitoring, maintaining, and enhancing applications to an external organization. The primary goal of an AMS is to ensure the smooth operation, availability, and optimal performance of applications, while relieving the burden of managing and supporting them from the organization using the service.
Why should businesses outsource their applications?
Based on our research, we have come up with the reasons why businesses outsource their systems and applications. The reasons below will help you make the right decision.
1. Cost Reduction
It can help businesses reduce IT costs by taking advantage of economies of scale and the expertise of third-party providers.
2. Increase focus on core business
This can free up internal resources so that businesses can concentrate on functions and strategic initiatives.
3. Access to specialized skills and expertise
This can give businesses access to specialized skills and expertise that they may not have in-house. It typically has a team of experts who are available 24/7 to respond to customer issues.
4. Enhanced operational effectiveness
Outsourcing can help businesses improve the efficiency of their IT operations by leveraging the expertise and resources of third-party providers.
5. Increased uptime and availability
Outsourcing can help businesses improve the uptime and availability of their applications by partnering with providers that have a proven track record of reliability.
6. Improved security and protection
It can help businesses improve the security and protection of their applications by partnering with third party providers that have a strong focus on security.
7. Compliance with industry regulations
Outsourcing can help businesses comply with industry regulations by partnering with providers that have experience working with regulated industries.
Tips to Consider before choosing your AMS Provider
Before outsourcing your application to third parties, you should consider these factors to choose the right fit for you. When you have a proposal or are searching for an AMS provider, make sure they have the below skills and offers to move further.
- Look for their experience in your specific industry. Check their track record, and any relevant certifications or partnerships.
- Consider your current and future needs. Ensure the AMS provider can scale their services as your application requirements grow. They should have the capacity to handle increased workloads, additional applications, or changes in your IT environment.
- Evaluate the provider’s support channels. They should offer reliable and responsive support, including incident management, problem resolution, and user assistance.
- Understand the pricing model of an AMS provider. Compare their costs against the services and features they offer. Look beyond the price tag and evaluate the value they provide.
By considering these four factors, conducting thorough evaluations, and engaging in meaningful discussions with potential AMS providers, you can make an informed decision and choose a partner that aligns with your application management needs and supports your business goals.
Recommended for you: How Can Managed Services Leverage Cloud Investments?
Which industries drive AMS support?
The global AMS market is projected to reach $393.72 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 7.1% from 2021 to 2028.
- The healthcare industry is the largest vertical for AMS, accounting for 22%.
- The financial services industry is the second largest vertical for AMS, accounting for 18%.
- The retail industry is the third largest vertical for AMS, accounting for 14%.

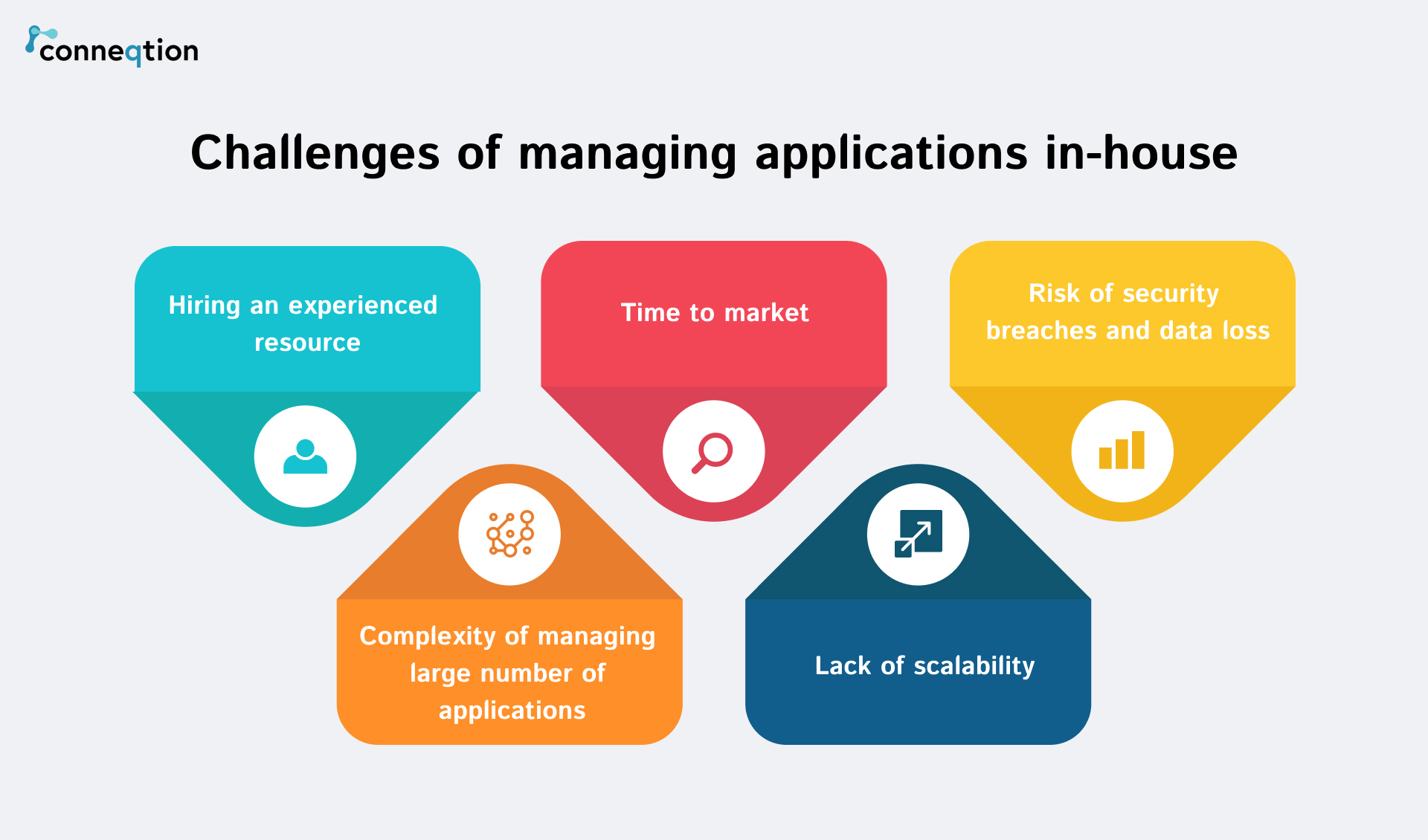
What are the challenges faced by in-house businesses while managing their applications?
#1 Hiring an experienced resource
Finding and hiring experienced professionals with the necessary skills to manage applications can be a challenge. The competition for top talent in the IT industry can make it difficult to attract and retain skilled application management professionals. Also, it involves significant costs, infrastructure and hardware expenses, software licenses, and ongoing maintenance. Budget constraints may limit the ability to invest in the latest technologies or provide round-the-clock support.
#2 Time to market
In-house application management teams are facing pressure to deliver new applications or updates when their competitors are going fast. Managing the entire application lifecycle, including development, testing, deployment, and ongoing maintenance, requires effective project management and coordination to meet business demands.
#3 Risk of security breaches and data losses
The implementation of robust security measures to protect against potential security breaches and data loss. However, without specialized security expertise and resources, in-house teams may face challenges keeping up with evolving threats and ensuring comprehensive security protocols.
#4 Complexity of managing many applications
In organizations with a diverse portfolio of applications, managing multiple systems, technologies, and integrations can be highly complex. In-house teams may find it difficult to effectively handle the complexity and interdependencies of various applications, resulting in operational inefficiencies or errors.
#5 Lack of scalability
In-house application management may struggle to scale rapidly in response to changing business demands. Scaling resources, infrastructure, and support services to accommodate increased workloads or sudden spikes in user activity can be challenging for in-house teams that have limited scalability options.
Key Difference between MSP and AMS
MSP and AMS are two different types of application management services. MSP stands for Managed Service Provider, while AMS stands for Application Management Services.
- MSP is a broader term that encompasses a wide range of services, including application development, maintenance, and support. MSPs can also provide IT infrastructure and operations services.
- AMS is a more specialized type of service that focuses on the management of applications. AMS providers typically have expertise in a specific industry or application.
In short, if a business wants to manage their IT infrastructure, they can choose a managed service provider. If a business wants specialized application management, they can opt for AMS.
Conclusion:
Overall, the future of application management services is bright. By adapting to the changing needs of businesses and leveraging new technologies, application management service providers can continue to play a vital role in helping businesses succeed in the digital age. We at Conneqtion Group have a year of experience in multiple industries. If you are searching for an AMS provider, get in touch with us to see better results for your application.




vishnu
Keep up the great work! Thank you so much for sharing a great post.