Understanding debit memos in Oracle Financials Accounts Payable can seem daunting, but it’s quite simple. Many people mistakenly believe that creating a debit memo is a complicated process. To clear up this misconception, we’re going to walk you through the steps and demonstrate just how straightforward it is.
By the end of this blog, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to efficiently manage debit memos within the Oracle Financials Accounts Payable subledger.
Business case for creating a debit memo:
Goods were purchased for the supplier worth $ 200. An invoice was created and accounted for in the books of accounts. However, later it was realised that goods worth $50 were defective and hence were returned to the supplier. In this case, the entity will create the debit memo against the originally issued invoice as now net amount payable to the supplier is $150 and not $200.
Step 1: Create an invoice.
Step 2: Creating a debit memo against a pre-created invoice in Oracle Fusion:
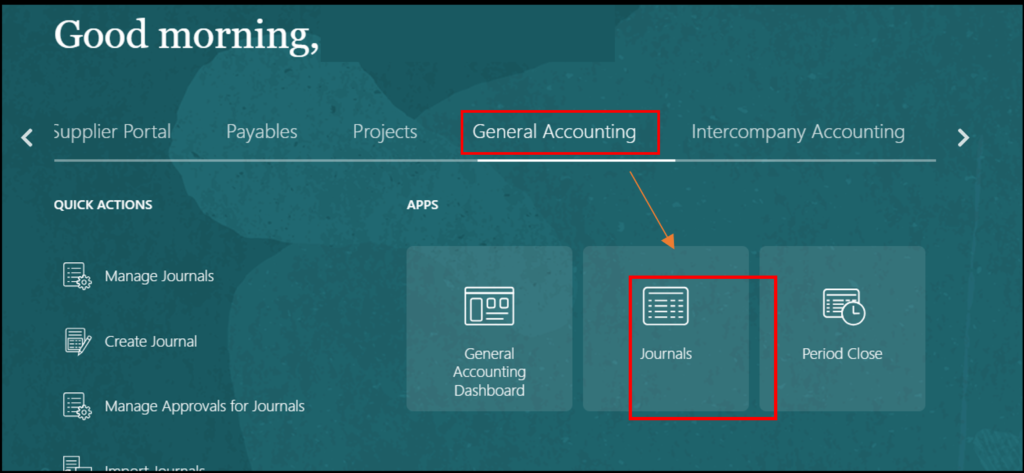
Navigation: Home> Payables> Invoice> task list> Create invoice
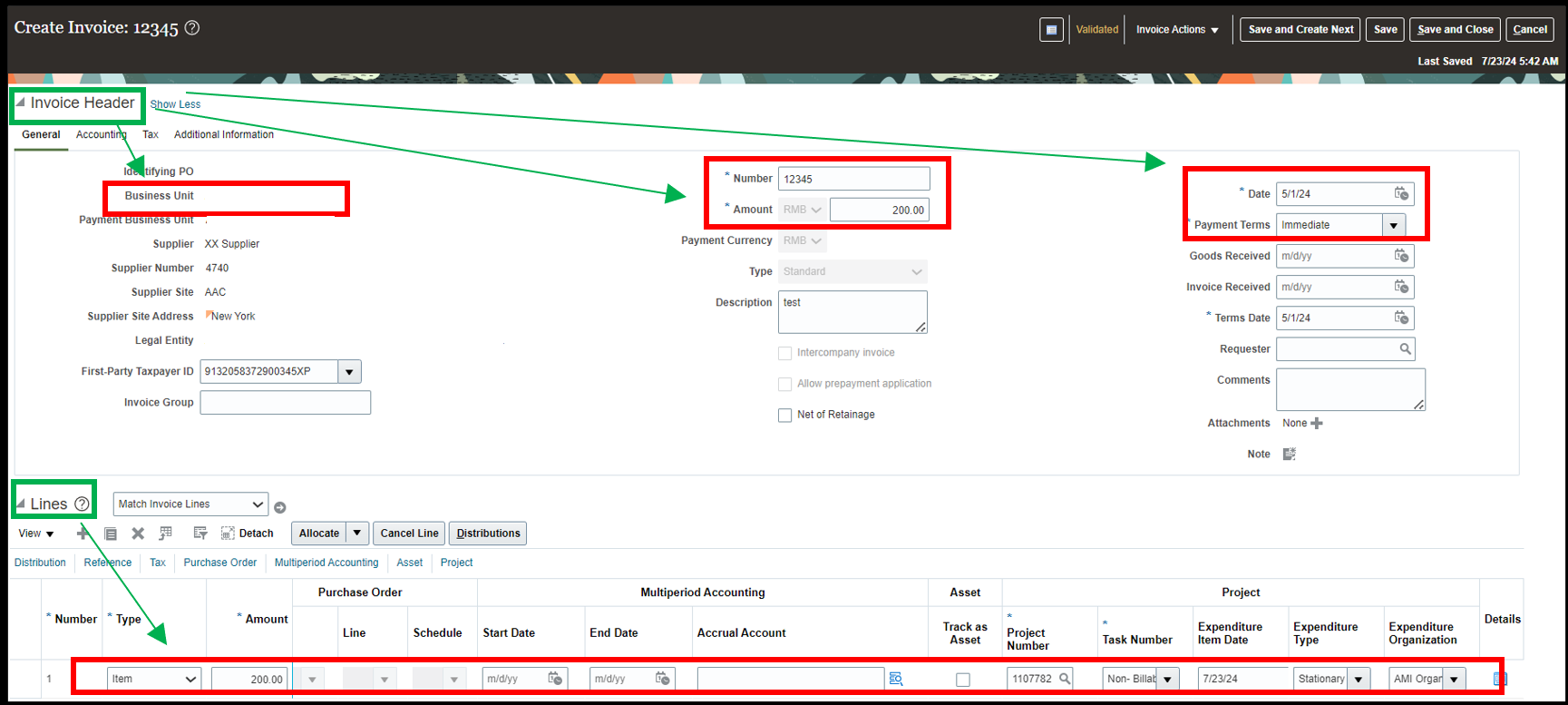
Step 2.1: Fill the Invoice Header level details
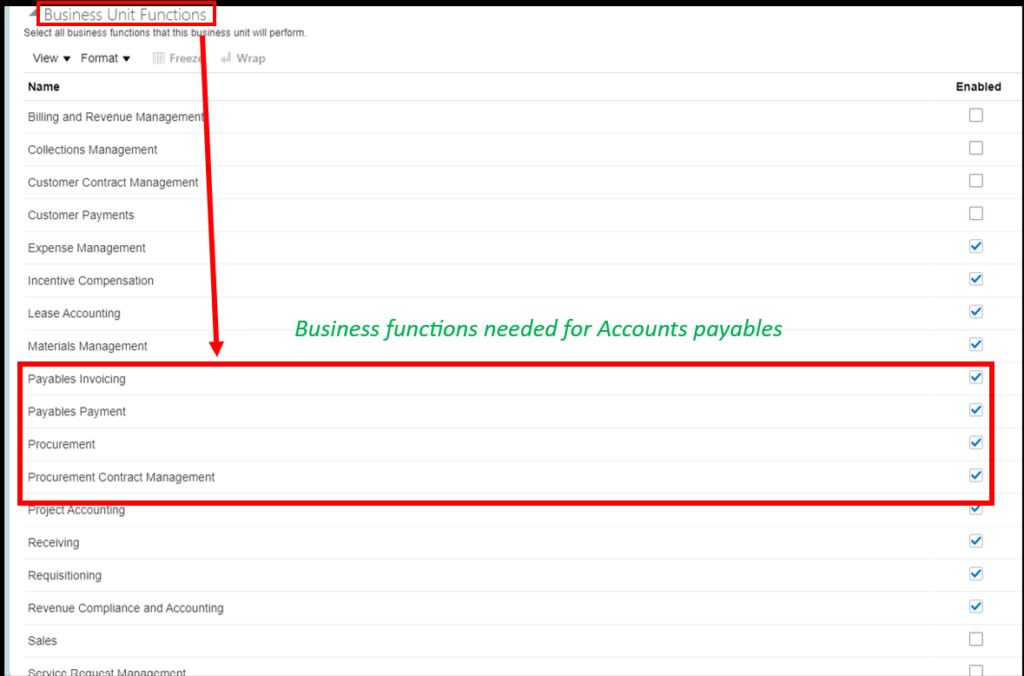
Business Unit: The BU in which the debit memo needs to be created. A Business unit is meant for transactional data security.
Supplier: The supplier for whom the debit memo is being created.
Supplier Number: A unique number being allotted to each supplier. This is meant for the purpose of identification of the supplier.
Supplier Site Address: The supplier can send goods from various locations/ site. In this icon, the user will provide the details from where the product is coming.
Legal entity: The legally registered entity of the supplier which is linked with the company.
Also Read: Accounts Payable Process of a Business and Its Invoicing Method
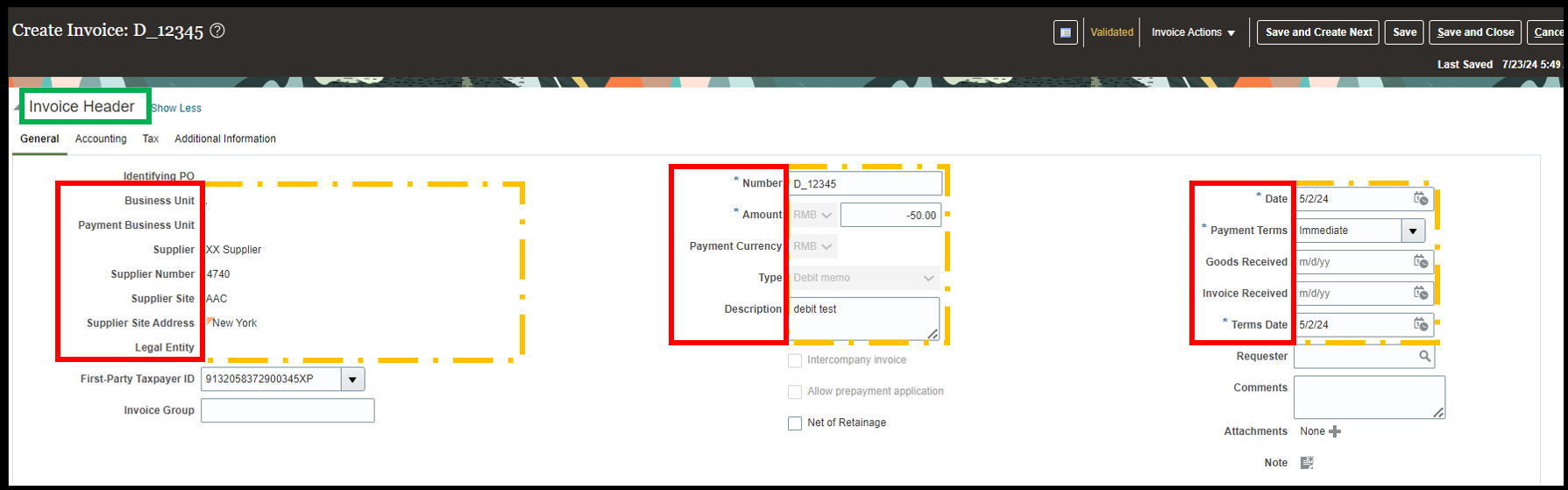
Number: It represents the Debit memo number that needs to be allotted for its recognition. For convenience, the number can be kept like the Invoice number for which the debit memo is created.
Amount: In case of Debit and Credit memo, the amount entered must be with a negative sign as they lead to a decrease in the amount payable to the supplier.
Payment currency: The currency in which the debit memo needs to be created.
Type: In case of a debit memo, the user needs to select the type as debit memo.
Description: Here the user needs to write the details/ reasons for creating a debit memo.
Date: The date on which the debit memo is created. Accounting date is different from the entered date as on the accounting date, the transaction is posted in the books of accounts. Hence, accounted date may or may not be same as the entered date.
Payment terms: If the business logic is concerned the objective of creating a debit memo is to rectify the payment mistakes. Hence, technically it should be IMMEDIATE. However, the system allows the user to define his own payment terms as well.
Goods received: It is the date on which the goods are physically received by the entity.
Invoice received: The date on which the invoice is received by the entity from the supplier.
Term date: It is the maturity date calculated for the date of receipt or invoice/ or transaction entry etc. This is calculated based on the payment terms.
Step 2.2: Select the Invoice that needs to be adjusted against the debit memo.
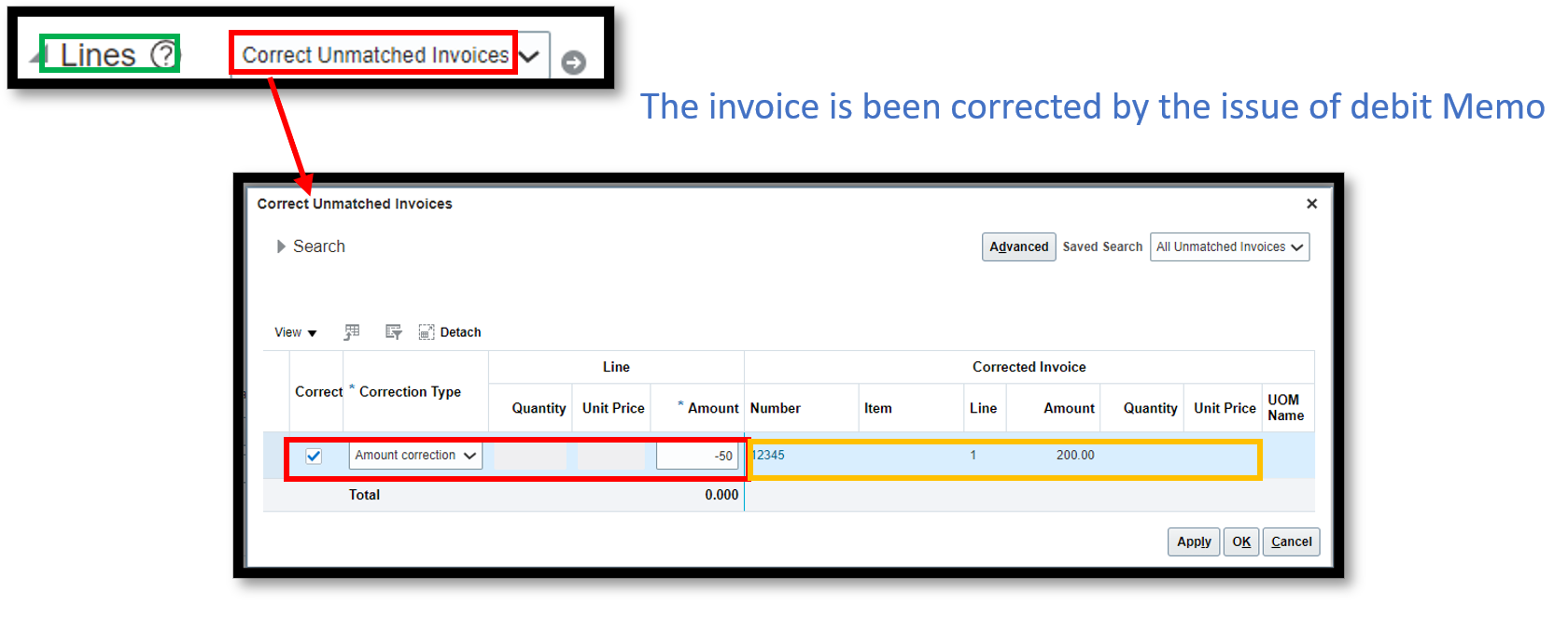
The invoice that needs to be correct is selected.
Step 2.3: Fill the invoice Line level details:
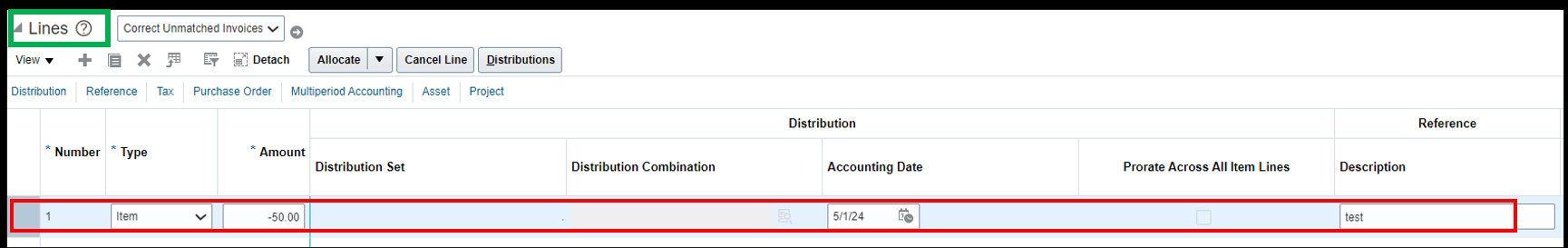
Number: It represents the line number.
Type: Whether the line is created for Item, Freight or miscellaneous.
Amount: It is the amount of the debit memo that needs to be adjusted against the invoice. It is mentioned in negative as it leads to the decrease in the amount payable to the supplier.
Distribution combination: In this case, since the amount is adjusted against the original invoice. Hence, the distribution combination does not need to be entered.
Accounting Date: It is the date on which the transaction needs to be accounted in the books of accounts.
Description: It explains the reason for the creation of the debit memo.
Once the debit memo is created, the amount on the original invoice will decrease.
Once created, the user needs to validate the Debit Memo.
Navigation: Top Right -> first step is to save -> then next step is to go to Action -> Validate
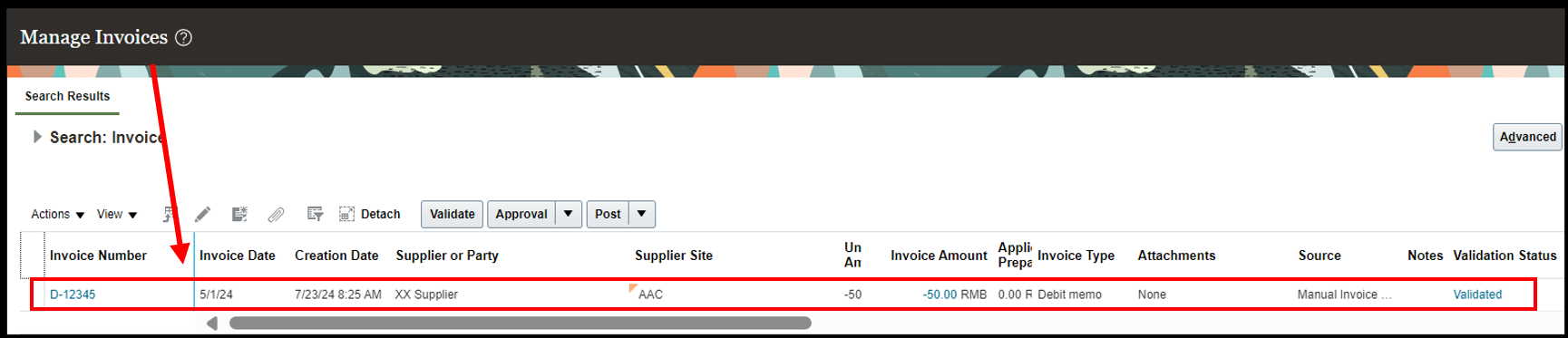
Step 3: View Debit memo on the Manage Invoice
After validation of the invoice, the debit memo can be checked on the ‘Manage Invoice’ page.
Navigation: Home -> Payables -> task list -> Manage Invoice -> Enter the Debit memo number in Invoice number.
Step 4: Create accounting for the debit memo:
Navigation: Home -> Payables -> Invoices -> Task list -> Manage Invoice -> Search Debit memo
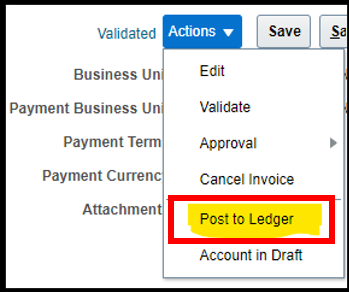
For accounting, the debit memo must be saved, validated and approved (optional based on the business needs). Only after the invoice is approved, it can be posted to ledger and thereafter accounting will get auto generated. Alternatively, user can perform auto-posting by running a schedule process under the monitor processes.
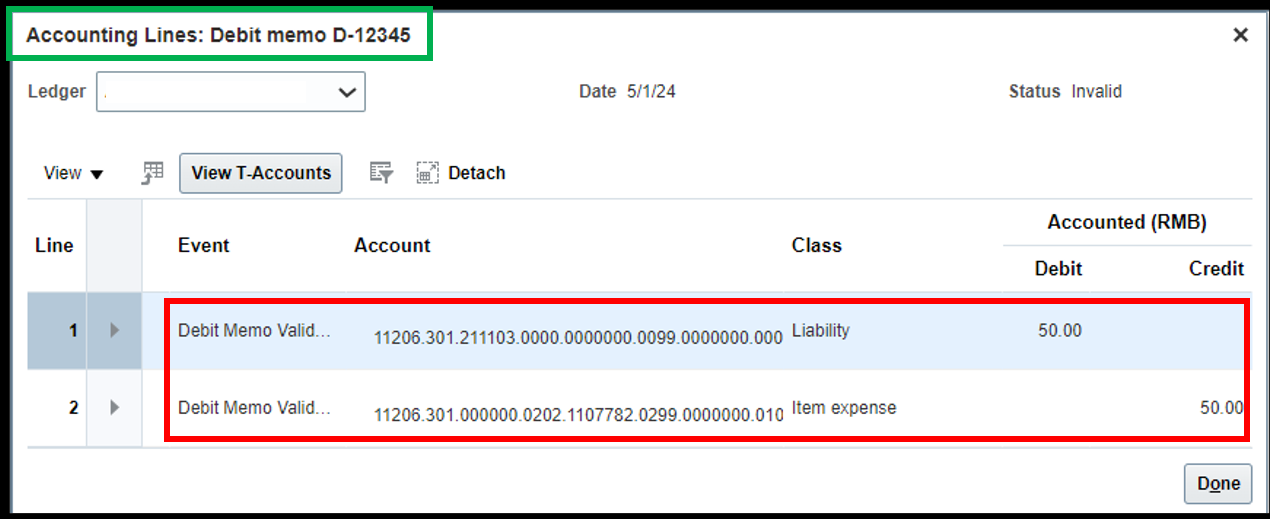
Relationship between Debit memo and Credit Memo:
- •In Oracle Cloud AP context, debit memos and credit memos are used as adjustments. These adjustments reflect the adjustments in the balances of the suppliers.
- •Both the debit memo and the credit memo have the negative creation sign.
- •Both have the same net accounting impact in the books of accounts. The Journal entry is Liability Account Dr to Expense/Inventory Account CR.
- •Only difference between the Debit memo and the Credit memo is on the basis of the initiator of the document. If the document has been created by the supplier, then it is called as a ‘Credit memo’. Alternatively, if the company itself is the initiator, then it is called as a ‘Debit memo’.
If you have any questions or concerns, please get in touch with us on [email protected].