A recent study suggests that the market size of cloud migration services is projected to expand at a CAGR of 22.3% during the forecast period, with an estimated global value of USD 16.52 billion by 2027. This article will delve into the essential characteristics of cloud data migration, the approach to execute a prosperous migration, the obstacles involved in the process, and the best practices for a seamless transition.
What is cloud data migration?
Cloud data migration is the process of transferring digital data from an on-premises or legacy IT infrastructure to a cloud platform. It involves the movement of data from one location to another, such as from a physical server to a virtual machine or from one cloud provider to another. The goal of cloud data migration is to enable organizations to leverage the scalability, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility of cloud computing while minimizing disruptions to their operations.
Reasons for migrating to cloud from on-premise
Cloud data migration has become increasingly popular due to a variety of reasons. Here are some of the main benefits and reasons why organizations choose to migrate their data to the cloud.
Cost savings: Moving data to the cloud can often result in significant cost savings as it eliminates the need for on-premises hardware and maintenance costs. Additionally, cloud providers often offer flexible pricing models that allow organizations to pay for only the resources they use.
Scalability: The cloud provides organizations with the ability to quickly and easily scale their storage and compute resources to meet changing business needs. This can be particularly valuable for organizations with fluctuating demand for their applications and services.
Data security: Cloud providers invest heavily in security, which can be a significant advantage for organizations with limited IT resources. By migrating data to the cloud, organizations can often improve their data security posture and reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
Business agility: The cloud provides organizations with the ability to quickly and easily spin up new resources and applications, which can be particularly valuable for organizations looking to experiment with new business models or quickly respond to changing market conditions.
Disaster recovery: By storing data in the cloud, organizations can often improve their disaster recovery capabilities. Cloud providers typically offer robust backup and disaster recovery solutions that can help organizations quickly recover from data loss or system failures.
Also Read: Top 10 Factors To Consider For EBS To Oracle Cloud Data Migration
How does data migration to the cloud work?
Migrating data to the cloud involves transferring data between storage systems, computer systems, or data formats. The process requires a clear understanding of applications used in the company, which can be done by auditing digital assets to identify the scope of the migration.
There are several types of data migration, such as storage migration, which involves transferring data from one storage repository to another and can take place on premises or in cloud environments. This type of migration is generally considered the most straightforward, but still requires a solid migration strategy.
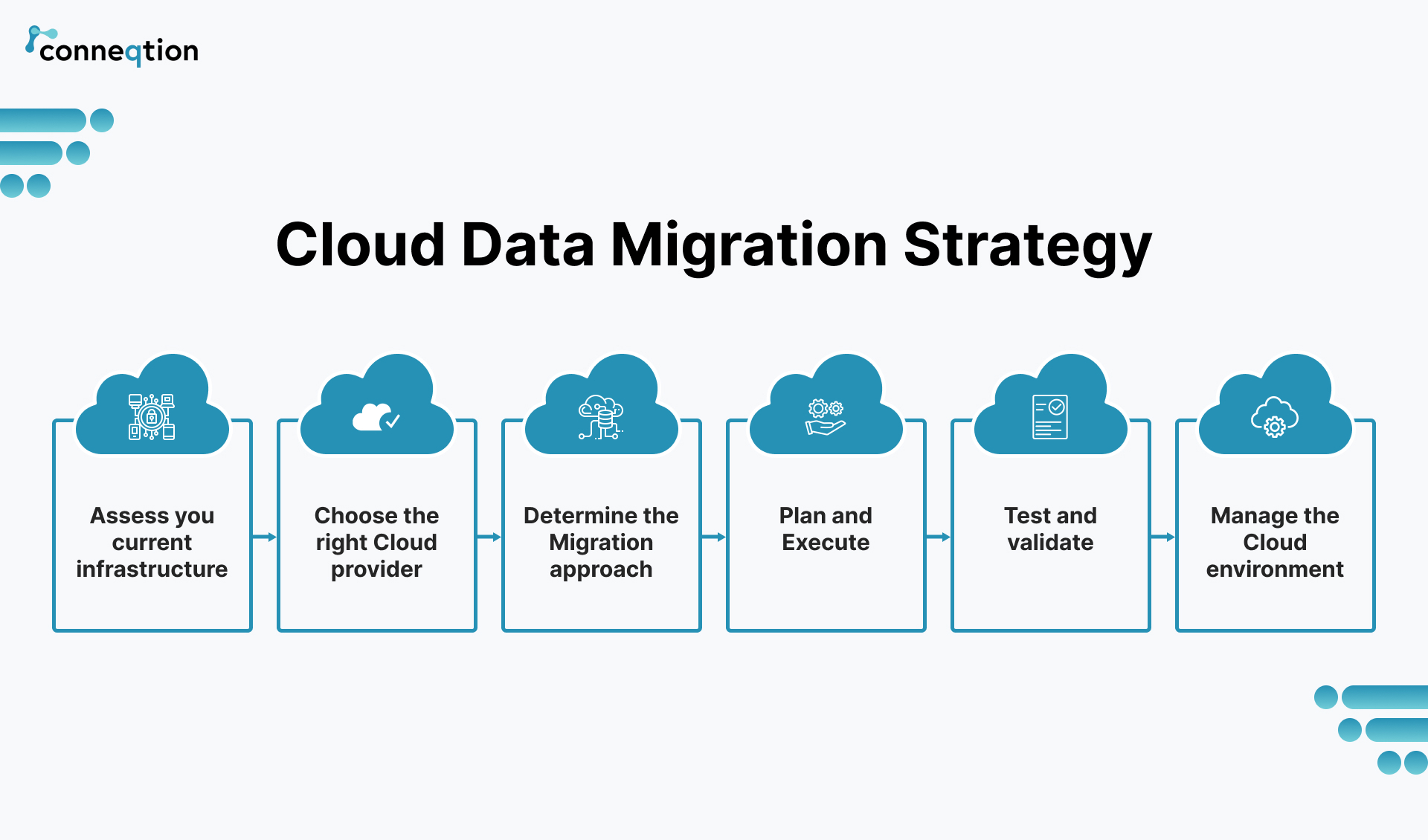
Cloud Data Migration Strategy
- Assess the current system: The first step is to evaluate the existing infrastructure, applications, and data that will be migrated to the cloud. This involves identifying what data and applications will be migrated, the size of the data, the current hardware and software configurations, and any potential compatibility issues with the cloud platform.
- Choose the right cloud provider: Once the assessment is complete, the next step is to select the right cloud provider that meets the organization’s requirements. Factors to consider include the provider’s reputation, security measures, pricing models, and support options.
- Plan the migration process: With the cloud provider selected, the next step is to plan the migration process. This involves defining the migration approach, creating a detailed project plan, identifying the data migration tools and techniques, and setting timelines and milestones.
- Test the migration process: Before executing the migration, it is important to test the process to ensure that it will work as expected. This involves creating a test environment to simulate the migration process, verifying data integrity, and testing the applications to ensure that they work correctly in the cloud environment.
- Execute the migration process: Once the testing is complete, the actual migration process can be executed. This involves transferring the data from the on-premises environment to the cloud environment using the migration tools and techniques identified in the planning phase.
- Monitor and optimize the migrated data: After the migration is complete, it is important to monitor the performance and optimize the migrated data to ensure that it meets the organization’s requirements. This involves monitoring the data for any issues or performance problems and implementing any necessary optimizations.
By following these steps, organizations can ensure a smooth and successful cloud data migration that meets their requirements and maximizes the benefits of the cloud.
Conclusion
Cloud data migration can be a complex process that requires careful planning and execution to ensure that the data is moved securely, efficiently, and without any loss or corruption. We at Conneqtion worked with various organizations from different locations which we have inhouse data migration tool to automate data entries in Oracle and provides reconciliation report. Contact us today for your organization’s cloud data migration process.